Space Flight Laboratory (SFL) confirmed that six radio frequency geolocation microsatellites developed for HawkEye 360 of Herndon, Va., successfully communicated with ground control.
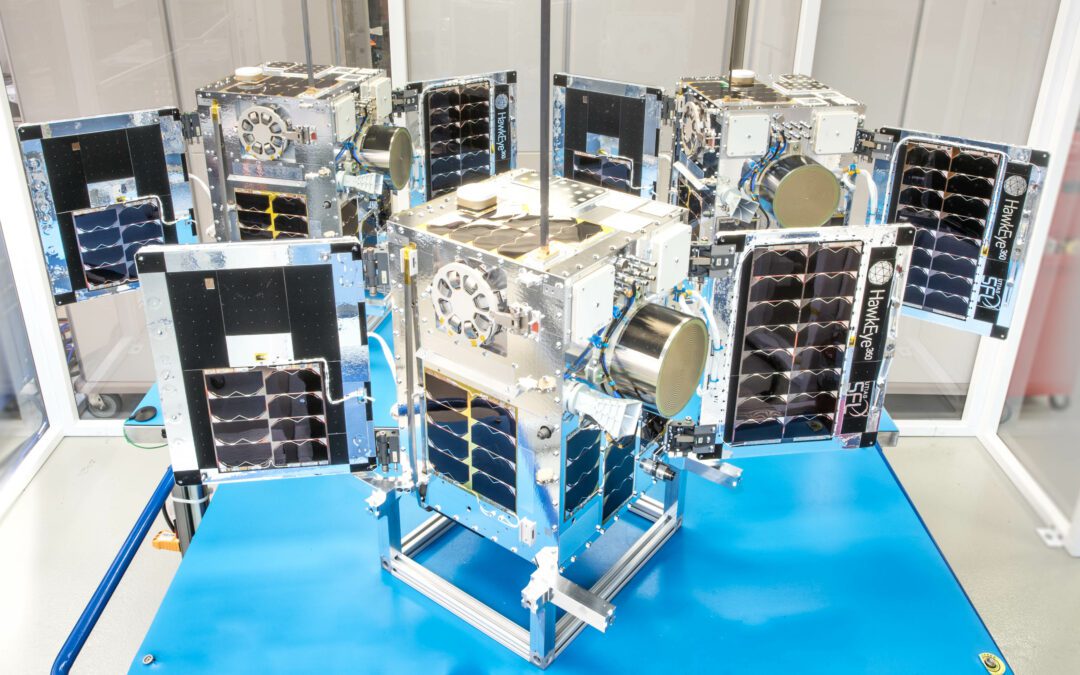


Space Flight Laboratory (SFL) confirmed that six radio frequency geolocation microsatellites developed for HawkEye 360 of Herndon, Va., successfully communicated with ground control.
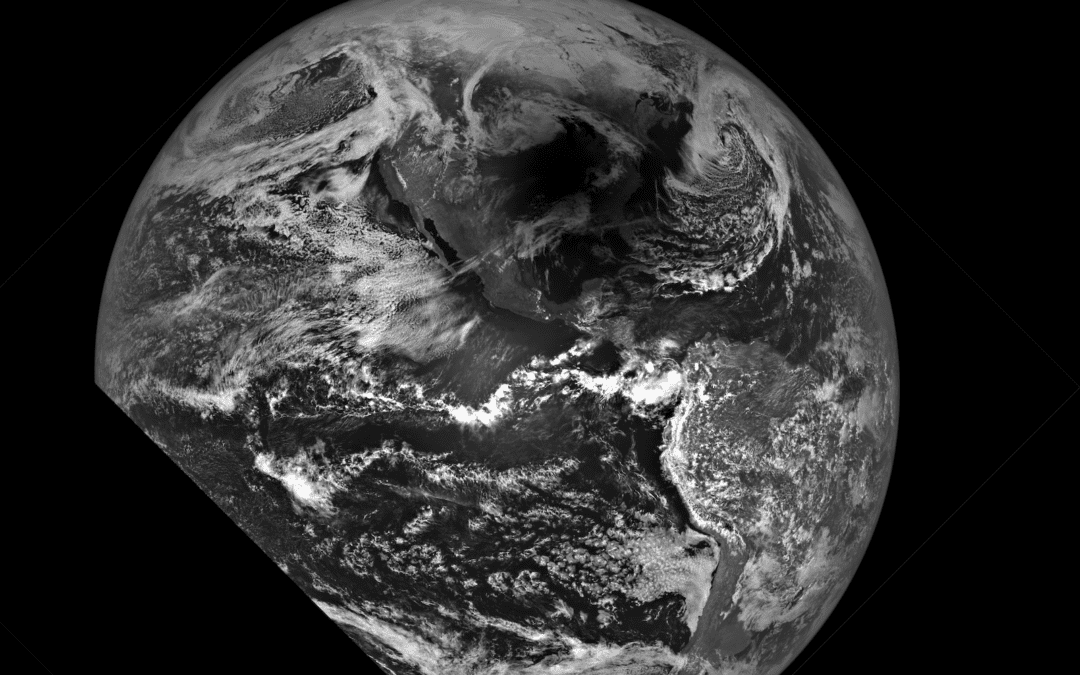
This spectacular image showing the Moon’s shadow on Earth’s surface was acquired during a 20-second period on April 8, 2024, by NASA’s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter.
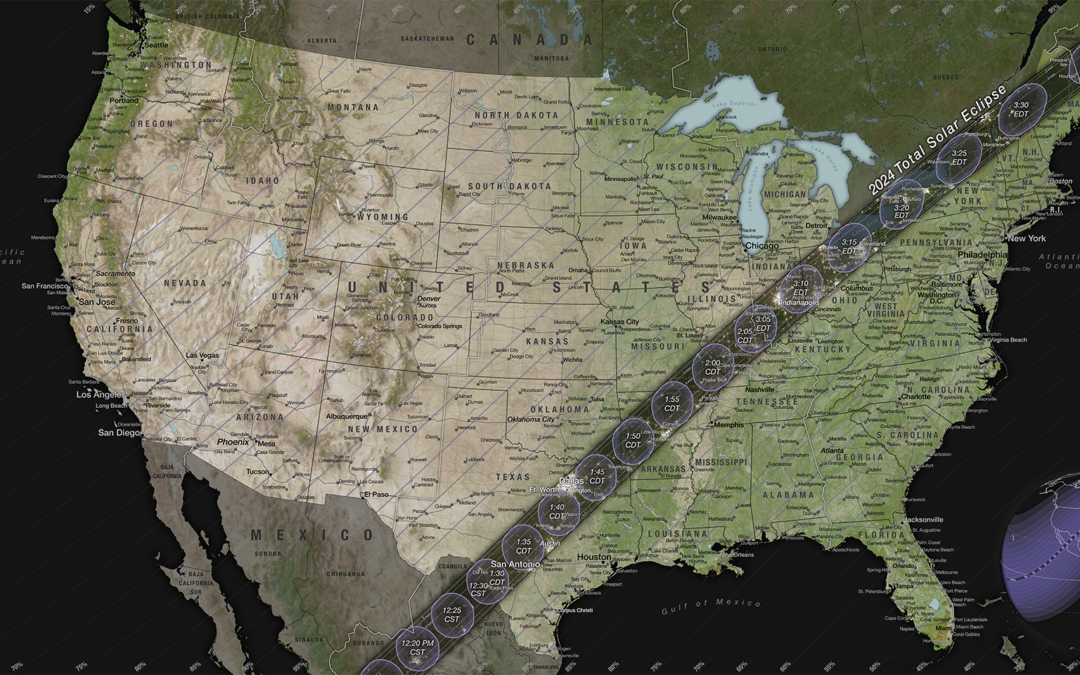
On April 8, 2024, most of North America will have the chance to see the Moon pass in front of the Sun during a solar eclipse.
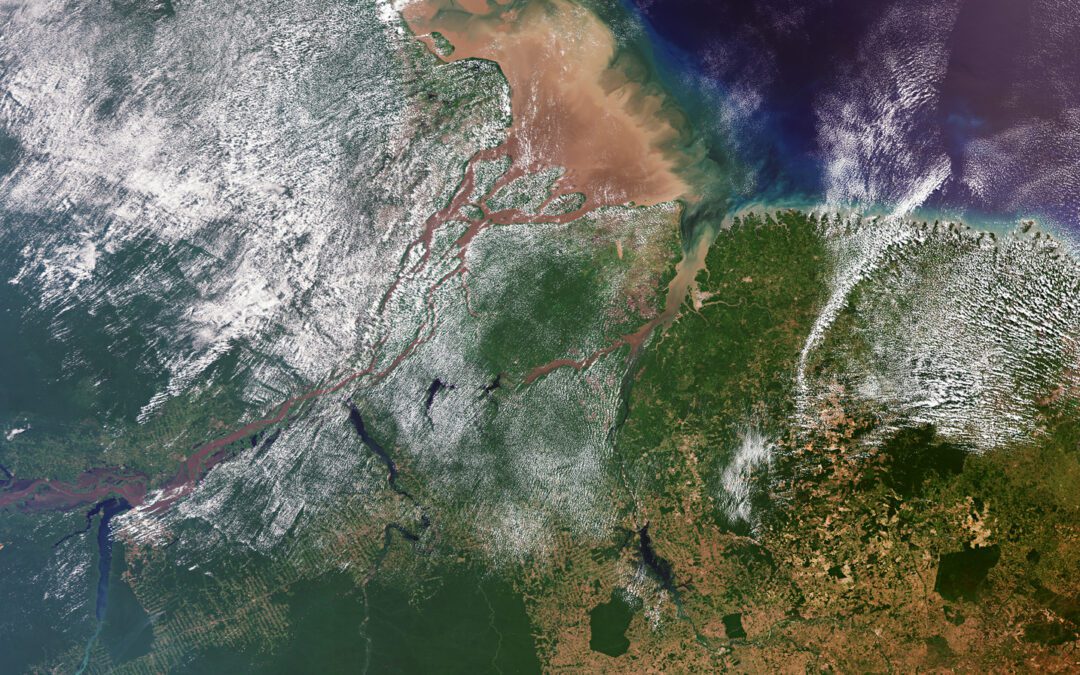

The Copernicus Sentinel-3 mission collected this image over northern Brazil, where the Amazon River meets the Atlantic Ocean.
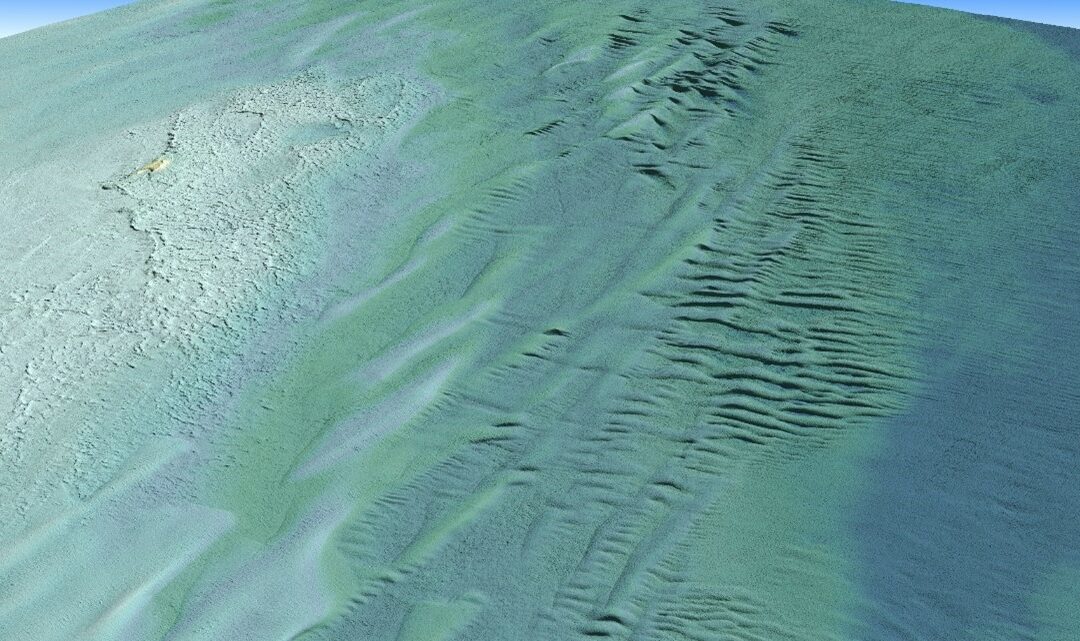

Tetra Tech Inc. used a Teledyne Optech CZMIL SuperNova Topobathymetric lidar system to successfully complete a project for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) to update all its bathymetric maps in the Great Lakes region, which includes refined maps of the marine ecology.
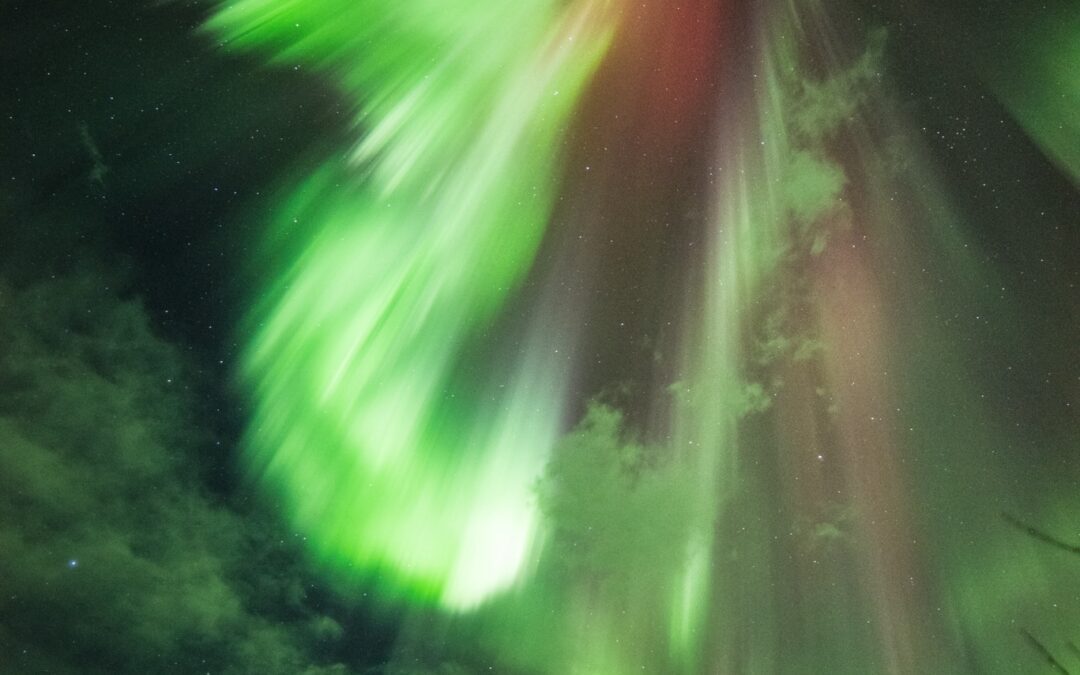

These colorful ribbons of light are the visible manifestation of the solar wind—the flow of charged particles from the Sun—interacting with the Earth’s magnetosphere.
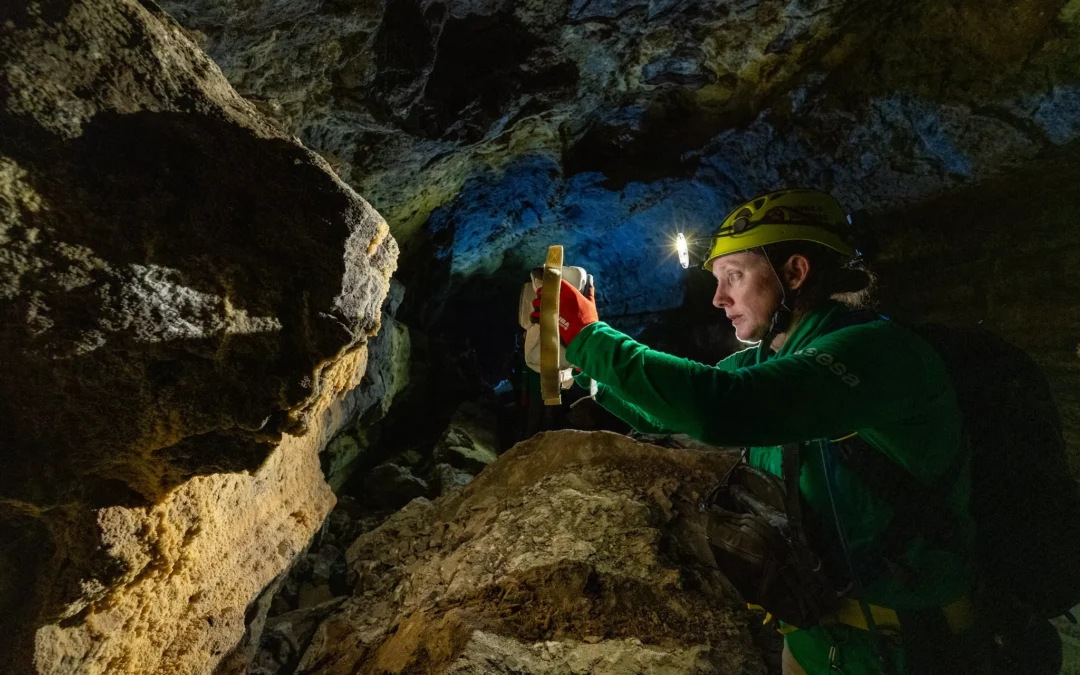

When NASA sends astronauts to the South Pole region of the Moon for the first time with its Artemis campaign, they will capture photos with a handheld camera to help advance scientific research and discovery for the benefit of all.
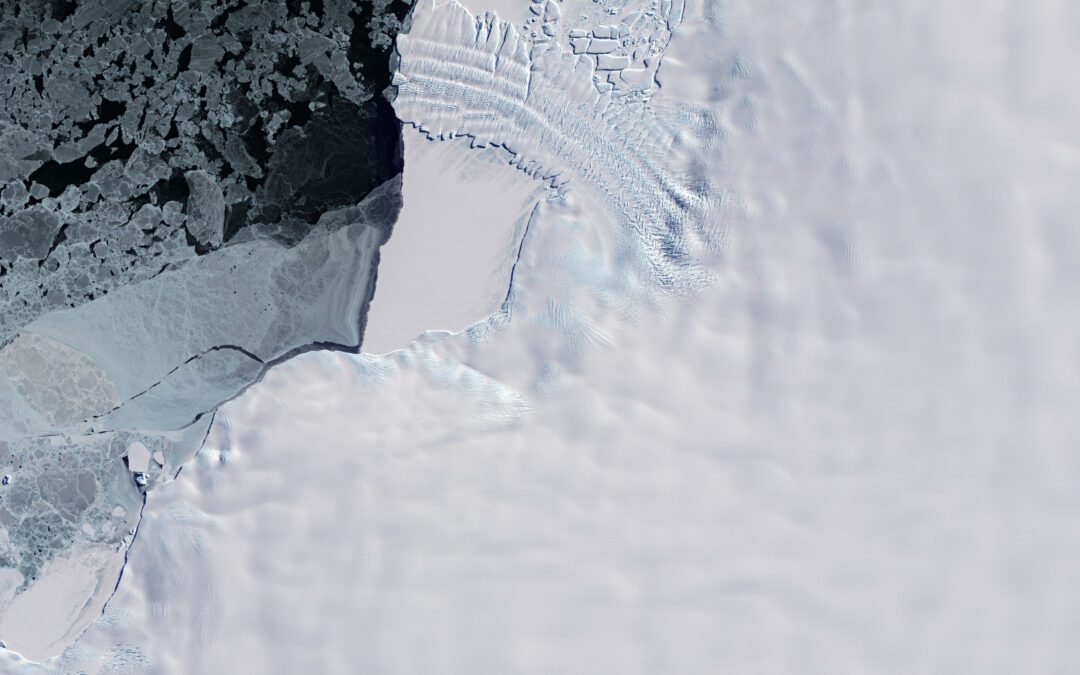
This Copernicus Sentinel-2 image features the ice tongue of the Dawson-Lambton Glacier in Antarctica, which lies southwest of the Brunt Ice Shelf in the Weddell Sea sector of the continent.
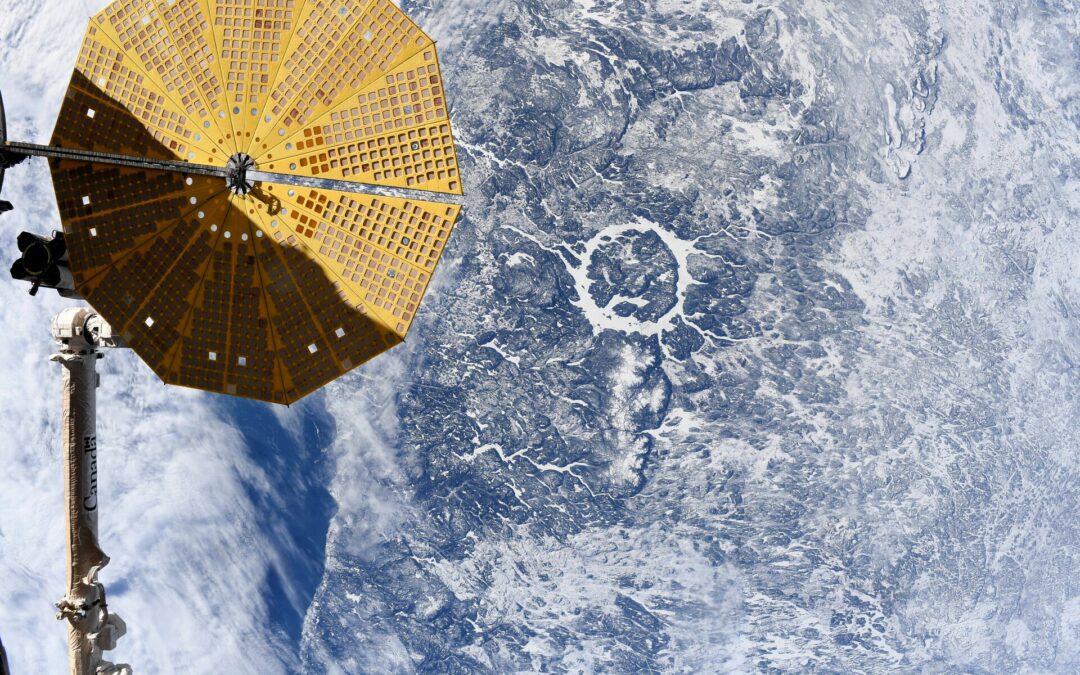

Manicougan Crater seen from the International Space Station on Feb. 5 2024, by ESA astronaut Andreas Mogensen.

Before and after satellite images from the Copernicus Sentinel-1 mission show the scale of the oil spill that occurred off the shores of Trinidad and Tobago’s coastline in February 2024.