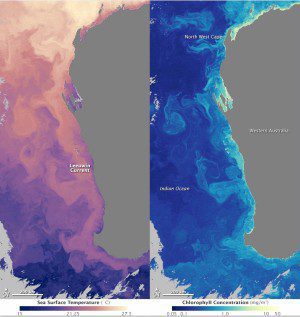
Though invisible to the naked eye, the warm current stands out in measurements of the temperature of the ocean's surface, as shown in the left image acquired by NASA's Aqua satellite on June 6, 2014. Warmer water is orange and pink, while cooler water is purple. In the right image of ocean chlorophyll, however, the ocean is clearly in full bloom. Acquired on June 6, 2014, by the Aqua satellite, the image shows high concentrations of chlorophyll in yellow and lower concentrations in blue. The highest concentrations are aligned with the warmest parts of the current.
Flowing south along Australia's western shore, the Leeuwin Current is an oddity. Unlike most currents that flow along the western shores of continents, it flows toward the pole (away from the equator), carrying warm tropical water into what would otherwise be a cold ocean.
The current hugs the coast, curving south and then east with the coastline. It is the world's longest coastal current, extending 5,500 kilometers (3,400 miles) from the North West Cape to the west coast of Tasmania”roughly equivalent to the distance between San Francisco and Miami.
The heat the current transfers to southern Australia moderates the climate, making it hospitable to marine species normally found much closer to the equator. Its warmth also encourages rain to form and fall over western Australia, saving it from the extreme dryness found on the southwestern shores of the other southern continents. Without the current, western Australia might resemble South America's Atacama Desert or southern Africa's Namib Desert.
While the current makes southern Australia hospitable, it normally turns the ocean into a desert. The warm water contains limited nutrients to sustain plant life, and it represses upwelling, so surface waters seldom get recharged with nutrients from the ocean floor. Without nutrients, few phytoplankton grow. Because plankton are the base of the food chain, only small populations of fish are able to live in the warm waters.
Image courtesy of NASA.

