ASPRS Approves LAS 1.4 Specification
The American Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing (ASPRS) board of directors approved LAS 1.4, a new release of the open file format for light detection and ranging (LiDAR) data storage and delivery. ASPRS has been maintaining and updating the widely used specification since its inception in 2001.
The most significant of the new features include:
¢ Expansion of the Class field from 32 to 256 classes
¢ Well Known Text (WKT) encoding for coordinate reference system designation
¢ Support for scanner designation for multiple sensor laser systems, such as mobile mappers
¢ Support for up to 15 return pulses for discrete pulse systems (waveform support was added at release 1.3)
¢ Maximum file size increased from 4GB to a theoretical file size of 18 EB
The full specification can be downloaded from the ASPRS Web site at www.asprs.org/LAS_Specification.
Astrium Wins ESA Earth Observation Contract
Astrium has been selected by the European Space Agency (ESA) as prime contractor for the Sentinel-5 Precursor (S5p) satellite, a low-cost mission to monitor atmospheric chemistry.
S5p is part of the Global Monitoring for Environment and Security program (GMES), which is a joint undertaking of the European Commission andESA. Under GMES, S5p is a high-performance, single-satellite, low-cost mission that will bridge the observation gap predicted for when the current atmospheric chemistry measuring satellites ENVISAT andERS-2 reach the end of their operations.
With a launch scheduled for early 2015 and a seven-year lifetime, S5p will maintain the continuity of science data before the Sentinel-5 instrument becomes operational toward the end of this decade. The Sentinel 5 instrument is scheduled to fly on the MetOp Second Generation satellites in a polar orbit.
GeoDigital Acquires Powel
On Dec. 1, 2011, Norway's Powel AS sold the assets of its U.S. subsidiary Powel, Inc., to digital mapping, imaging and data acquisition services firm GeoDigital International, Inc. All current Powel employees, software assets, customers and facilities will form a new software and analytics division, GeoDigital Solutions, Inc.
GeoDigital integrates advanced imaging and data acquisition technologies to perform airborne and ground mapping services with light detection and ranging (LiDAR) technology for applications such as vegetation management and line rating and clearance analysis. Powel's applications, such as its StakeOut field design and VegWorks vegetation maintenance tools, are able to format spatial data collected by the GeoDigital systems into detailed asset inventories for field maintenance planning, execution and regulatory compliance reporting.
The combined organization will employ about 250 people across Canada and the United States. GeoDigital Solutions will maintain all current facilities, including Powel's St. Paul, Minn., headquarters. All existing sales and support structures will remain, and GeoDigital Solutions will support all existing Powel products, customers and long-term support commitments.
Pléiades 1A Successfully Orbited
A Soyuz launcher successfully orbited the Pléiades 1A satelliteDec. 16, 2011, from the Guiana Space Centre (CSG). The European Space Agency, the French space agency CNES and Arianespace jointly manageCSG.
Built by Astrium for CNES, the Pléiades constellation offers users 50-centimeter products with a ground swath of 20 kilometers, the largest in its class, and enhanced image location accuracy. Marketed by Astrium GEO-Information Services, Pléiades products will be available from March 2012.

Three days after its launch, Pleiades 1A returned this image of the Hassan II Mosque in Casablanca, Morocco.
The first of a new generation of satellites operated by Astrium Services, Pléiades 1A will be followed between 2012 and 2014 by SPOT 6, its twin Pléiades 1B and finally SPOT 7. Built around a similar architecture and phased in the same orbit at 700 kilometers, the four-satellite constellation will ensure availability of 50-centimeter to 2-meter products to 2023.
Satellite Data Show Reduced Toxic Air Emissions
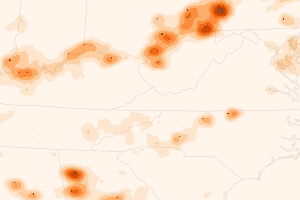 Satellite data combined with ground measurements indicate the Clean Air Interstate Rule, issued by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency in 2005, is working in several states.
Satellite data combined with ground measurements indicate the Clean Air Interstate Rule, issued by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency in 2005, is working in several states.
Scientists, regulators and the electric power industry came together to address pollution caused by sulfur dioxide (SO2), a key emission from coal-fired power plants that contributes to the formation of acid rain and to respiratory health problems. Scientists using the Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI) on NASA's Aura satellite observed major reductions in SO2 between 2005 (above) and 2010 (below) in Alabama, Georgia, Indiana, Kentucky, North Carolina, Ohio, Pennsylvania and West Virginia. Led by Vitali Fioletov of Environment Canada, the research team found that SO2 levels near the region's coal-fired power plants fell by nearly half since 2005.
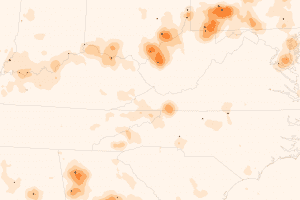
Scientists using the Ozone Monitoring Instrument on NASA's Aura satellite observed major reductions in sulfur dioxide between 2005 and 2010 in Alabama, Georgia, Indiana, Kentucky, North Carolina, Ohio, Pennsylvania, and West Virginia.
Scientists attribute the decline to the Clean Air Interstate Rule. The regulation capped emissions but left it up to power companies to determine how to reduce them. In response, many power plants installed desulfurization devices and took other steps to limit the release of SO2.
The new observations from the OMIconfirm ground-based measurements that had shown declining SO2 levels. The research also demonstrates how scientists could monitor emissions throughout the world, even in places where ground measurements are sparse.
Satellites Show Texas Groundwater Severely Depleted
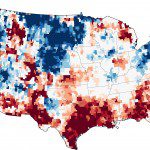
The maroon shading over eastern Texas shows that the ground has been this dry less than 2 percent of the time between 1948 and the present.
The record-breaking Texas drought that has fueled wildfires, decimated crops and forced the sale of cattle herds also has reduced the state's groundwater to its lowest levels in more than 63 years. At the end of November 2011, groundwater supplies were extremely depleted in more than half of Texas, as well as parts of New Mexico, Louisiana, Alabama and Georgia.
The map below is based on data from the twin satellites of the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE), which detects small changes in Earth's gravity field that are caused by the redistribution of water on and beneath the land surface. Scientists used a sophisticated computer model that combines measurements of water storage observed by GRACE with a long-term meteorological dataset to generate a continuous record of soil moisture and groundwater stretching back to 1948; GRACE has been recording data since 2002. The meteorological data include precipitation, temperature, solar radiation and other ground- and space-based measurements.
Sharper Satellite Images Guide Farmers Worldwide

The DMC constellation can cover whole countries every 2-3 days, which opens the door to near-real-time precision agriculture.
In the two years since DMC International Imaging Ltd. (DMCii) added 22-meter multispectral imagery to its geospatial data portfolio, the detailed satellite views of Earth's surface have proved to be valuable tools for farmers facing increasing pressures, including rising fertilizer costs.
Acquired from the latest generation of Disaster Monitoring Constellation (DMC) imaging satellites”UK-DMC2 and Deimos-1”this new class of data is employed every season for precision agriculture across numerous countries and accounts for 50 percent of DMCii's annual growth.
In precision agriculture, satellite data are used to gather precise knowledge of a farmer's land, pinpointing variations in crop growth and condition. The farmer is shown just where fertilizer or crop protection chemicals need to be applied and in what quantities. Global Positioning System-based instructions can be relayed directly to tractors and other automated farm equipment. The aim is to maximize crop yield and quality while minimizing production costs and environmental impact.
The 22-meter data produced by the two newest DMC satellites offer more detail, making the data suitable for much smaller field sizes. In addition, the higher-resolution images now have 10-bit instead of 8-bit pixels, yielding greater sensitivity in the DMC's three Landsat-compatible spectral bands of red, green and near-infrared.
United Kingdom Invests in Radar Earth Observation Satellites
On Nov. 29, 2011, U.K.Minister of State for Universities and Science David Willetts announced an investment of £21M that will enable British small satellite pioneer Surrey Satellite Technology Ltd. (SSTL) to build NovaSAR, a space-based synthetic aperture radar (SAR) remote sensing program. Once the NovaSAR constellation is operational, the U.K. government believes the fleet could yield a 5,000 percent return on investment during the coming decade.
Through an intensive development program, the combined expertise of SSTL on advanced small satellite platforms and Astrium UK's experience on radar payloads has created a new small SAR satellite that offers powerful radar remote sensing capabilities for approximately 20 percent of the cost of conventional radar missions. The government will provide the necessary seed funding alongside industry to develop and build the first NovaSAR demonstration satellite, which could be launched as early as 2013.
Government will contribute £21 million to assist in the development and launch of the first satellite, which if the project progresses as planned will leverage an additional £154 million of inward investment to the United Kingdom. Once the NovaSAR constellation is up and running, it's anticipated that this small government investment could yield a 50:1 return of £1bn during the coming decade.

