Advanced printing systems coupled with mobile capabilities offer geospatial users new tools for mission-critical applications.
By Bob Honn, director of Marketing Services, Wide-Format Printing Systems Division, Océ North America (www.oce.com), Chicago.
As today's workforce continues to go mobile, the industries that rely on geospatial applications, such as public utility management, urban planning, local and federal government and emergency management, are no exception. As work environments become more collaborative, the need to share, view and print geographic information system (GIS) and related documents from a variety of locations is growing. A powerful combination of advanced large-format printing solutions and the ability to access, update and print large-format geospatial documents in the field can yield multiple benefits.
Why Printing Matters
GISusers' primary responsibilities are to gather and analyze data, then draw conclusions from the data, so printing generally is an afterthought. This is unfortunate, because a hard-copy map is a highly effective visual tool for mission-critical applications, such as discussing information within a project team, presenting (internally or externally) information as part of a regulatory or approval process, or managing disaster recovery or emergency response situations.
Consider a common scenario: A river spills over its banks and poses a disastrous flood risk. All nearby homeowners and businesses must be notified immediately. The data needed to communicate the message include satellite and aerial imagery, geospatial information from the latest engineering flood plain survey, and county information. Such multijurisdictional information means that prints must clearly indicate the various jurisdictions to identify who is responsible for notifying homeowners and businesses. Additionally, printed maps are an invaluable aid for water crews to use in the field, because field crews must locate all water valves within each sector and make sure the affected areas don't contaminate the clean water supply.
Printing is a critical component to geospatial applications and can greatly impact a company's ability to do their job in a timely manner. It's imperative forGISusers to invest in large-format printing equipment that can help them fully realize the benefits of the latestGIStechnologies and enhance their own operations.
Large-Format Color Printing Solutions
GISplot files have been increasing exponentially in complexity and size, thanks to the growing use of high-resolution aerial and satellite imagery, detailed vector data, 3-D data and the sophisticated modeling capability of design software. On one hand, this means better maps that can support better decision making. On the other hand,GISusers often are hampered by the inherent limitations within their existing large-format print technology.
Frequent bottlenecks as a result of using traditional inkjet printing and plotting technology include slow print speed, extended drying time and expensive media requirements. To address these workflow-disrupting issues requires advanced large-format printing solutions that offer the following capabilities:
Powerful File Processing.
Systems that offer fast file processing enable quick, efficient printing of complex files containing imagery and data. Concurrent processing boosts project turnaround time by enabling the system to begin processing another job while it prints the first one.
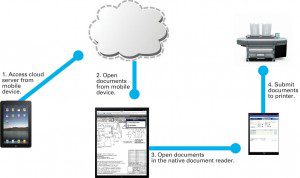
Storing geospatial documents in the cloud makes it easier for field users to access and print them through a variety of mobile devices.
Fast Speeds Equal Greater Throughput. The long print times per file from legacy inkjet systems, coupled with the time needed for heavy coverage maps, can stymie efficient workflow. In contrast, advanced color toner-based systems can deliver speeds of up to 1,300 square feet per hour”with zero drying time.
Increased Flexibility. With the ability to load multiple on-line media rolls”in some cases up to six”
users can print their project team maps, presentations and even water-resistant field maps without the manual roll changing required by legacy inkjet systems.
High-Quality Color. BecauseGIS applications are, by their nature, tied to maps, the need for outstanding color output can't be overlooked. The use of color is critical to effectively communicate detailed information in 3-D renderings,GIS maps and satellite images.
Advanced large-format color printing solutions help geospatial professionals work more efficiently. These systems can save users hours in their day previously spent printing and offer high-quality output, often justifying the equipment's acquisition cost. The most advanced systems also can be adapted to address the changing work environments of today's geospatial professionals, meeting new mobile work requirements.
Large-Format Printing Supports a Mobile Workforce
Because of the nature of their work, most geospatial professionals make decisions in the field. For example, public utility companies may need to access and print maps of underground power lines while on-site. Or, if an emergency incident occurs, local government officials may need to access maps of the affected areas while on the scene so they can provide updates to citizens, emergency response agencies and personnel.
Users must share and view geospatial data that are critical to making these decisions from a variety of locations via their mobile devices (e.g., iPad, iPhone and Android devices). New mobile print applications make this collaborative approach easy by leveraging the mobile device's Internet connection in conjunction with mobile printing software to access and print to any large-format enabled printer. This makes it easy for mobileGISprofessionals to share, manage and print content on the fly.
Sharing Documents in the Cloud
For sharing in a collaborative work environment, data first must be published to a data repository. For example, users can scan data to an FTP file and publish directly from a desktop to ADrive, Dropbox, Google Docs and Amazon Web Services solutions.
Using a scanner, users can scan via FTP to the cloud and store documents with a cloud provider of choice. This allowsGISusers to select providers that meet their storage and security requirements without being locked into a single proprietary service provider.
The only requirement is that the cloud storage provider must have an FTP front end that enables scan-to-FTP functionality; otherwise, uploading to a service provider is another option. As shown in the diagram above, once documents are stored in the cloud, the rest of theGISproject team can access and retrieve them using a variety of mobile devices for viewing and printing purposes.
View, Retrieve and Print Documents from the Cloud
Once documents are stored in the cloud, authorized project users can access the cloud server from their mobile device, open the stored documents they wish to view, prepare the documents to be printed and finally send the documents to any large-format printer enabled with mobile printing software. In most cases, all that's required is a mobile device equipped with an Internet or WiFi connection, a mobile print application and print manager service for the mobile device, and a cloud server account.
Creating a Flexible Workflow
Simply put, the ability to access, update and printGISdocuments in the field provides greater flexibility to professionals' workflow. For example, employees no longer have to worry that they have all theGISdocuments they may need stored on a jump drive or printed as hard copies before they go into the field. They can trust that all the critical documents they need are stored securely in the cloud, can be accessed from almost anywhere, and can be printed to any large-format printing system”located on the job site or a mobile workstation”enabled with the mobile printing software.
This workflow enables greater portability and reduces potential waste generated by printing documents that may or may not be needed. Mobile access and printing of documents also can lead to reduced downtime and reduced costs because employees don't need to put a job on hold while they leave the site to retrieve critical maps or data. This capability is especially important in the event of an emergency, as field-based workers can have instant digital and printed access to important maps and information on site in real time.
Additionally, with the use of the cloud, files don't need to be shared via email, a process that can be limited by the email server's capacity and the large size ofGISfiles. Also, there's no version control when multiple versions of the same files are shared via email, as a central repository in the cloud helps control this problem.
As companies continue to adopt an increasingly mobile and collaborative approach to their operations, they're looking for the latest tools to support their on-the-go workforce. Combining advanced large-format print systems with mobile print capabilities gives GISusers the flexibility to print high-quality, color maps in the field without disrupting their workflow. With this powerful capability, users can rest assured they'll always have immediate access to the documents they need when they need them.