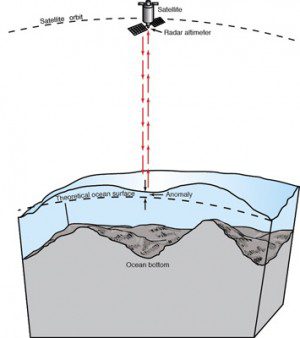
An Earth-orbiting radar can't see the ocean floor, but it can measure ocean-surface height variations induced by the ocean floor's topography. When interesting features are discovered in satellite measurements, they later can be surveyed in fine detail by ships.
CryoSat was designed to measure Arctic sea-ice thickness, but high-resolution mapping of ocean-floor topography now is being added to the ice mission's repertoire.
The main objective of the polar-orbiting CryoSat is to measure the thickness of polar sea ice and monitor changes in the ice sheets that blanket Greenland and Antarctica. But the satellite's radar altimeter can detect tiny variations in the height of the ice as well as measure sea level.
The topography of the ocean surface mimics the rises and dips of the ocean floor due to the gravitational pull. Areas of greater mass, such as underwater mountains, have a stronger pull, attracting more water and producing a minor increase in ocean-surface height. Therefore, instruments that measure sea-surface height incidentally map the ocean floor in previously uncharted areas.
Image courtesy of Scripps Institution of Oceanography.

