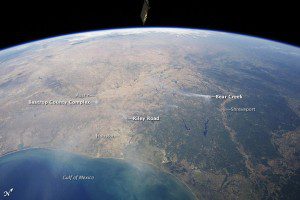
A Sept. 6 image, taken from the International Space Station (ISS) using a short focal-length lens (12 mm) to capture a wide field of view, shows smoke plumes to the east of Austin; to the north of Houston; to the northwest of Lake Sam Rayburn and Toledo Bend Reservoir; and to the west of Shreveport, La. Diffuse smoke is moving offshore into the Gulf of Mexico at image bottom. Part of an ISS photovoltaic radiator panel is visible at image top center.
Record-setting drought conditions have affected much of Texas since early 2011, drying out both forest and grassland and providing ample fuel for wildfires. Relatively high winds and low humidity levels also have contributed to the rapid spread and expansion of fires.
According to a report dated Sept. 7, 2011, the Texas Forest Service had responded to 172 fires affecting an area of 546.53 square kilometers (135,051 acres) over the preceding seven days. Fires near Bastrop (to the east of Austin) had destroyed 785 homes as of Sept. 7, 2011.
Image courtesy of the ISS Crew Earth Observations experiment and Image Science & Analysis Laboratory, Johnson Space Center. Caption by William L. Stefanov, Jacobs/ESCG at NASA-JSC.