Canada's RADARSAT Constellation Mission expands on RADARSAT's heritage to benefit a broad range of global consumers.
By David Belton, general manager, MDA Geospatial Services (www.mdacorporation.com), Richmond, British Columbia, Canada.
In January 2013, the Canadian government placed the future of its next-generation strategic monitoring and surveillance asset in the hands of MacDonald, Dettwiler and Associates Ltd. (MDA) with a contract to build and launch the RADARSAT Constellation Mission (RCM). The contract, which also tasks MDA to operate the mission during its first year, follows a series of MDA awards from 2004 to 2013 for various mission design phases.
RCM is a constellation of three C-band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) low Earth orbit satellites that extends Canada's commitment to the RADARSAT program. The initial mission design is for three satellites”scalable to six”allowing for changing requirements, increased demand and greater flexibility. The launch of all three RCM satellites on a single rocket is scheduled for 2018 from Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif.
Mission Objectives
The constellation will deliver unprecedented levels of high-repeat coverage over Canada's northern territories, three ocean approaches and inland waterways while providing daily access to 95 percent of the globe to Canadian and international users. Additional mission objectives include providing C-band SAR data continuity to existing RADARSAT-1 and RADARSAT-2 data users as well as to enhance the global operational use of C-band SAR data in existing and new user communities.
More than 90 percent of global trade moves across the world's oceans, making maritime surveillance a key issue for national security and the economy. RCM will directly support enhanced maritime surveillance for ship detection over large areas of Canada's maritime domain in the Arctic, Atlantic and Pacific oceans.
An Automatic Identification System (AIS) on each satellite, which, along with multiple imaging modes and polarization options, will more accurately detect and highlight vessels that aren't broadcasting their identity. This capability will drive more effective identification, tracking and interception of potentially illegal operations and maritime security threats for Canada as well as other governments sharing similar requirements.
Designed to Meet the Challenge
Maritime monitoring for a country the size of Canada presents an enormous challenge. With immense coverage areas and hundreds of thousands of potential targets in often remote, inhospitable locations, RCM's constellation approach, with daily revisits and wide-swath imaging capabilities, directly addresses the challenge. The imaging capacity of each individual RCM satellite has been sized to exceed all of the Canadian government's imaging needs by a factor of two, ensuring commercial users have the opportunity to task the satellites to monitor large areas around the world on a regular basis.
RCM will be able to repeat wide-area coverage of shipping lanes and key port facilities in less than 24 hours. With RCM, the ground track repeat will be reduced to four days due to having three satellites in a 12-day ground track repeat. The implications for these significant changes to revisit times are enormous for defense and civil users around the world.
Expanding Capabilities Create New Opportunities
RADARSAT missions have spawned a large and loyal international user community since RADARSAT-1's launch in 1995. RCM extends the legacy of the RADARSAT missions while leveraging the developing trend in satellite remote sensing toward satellites that are interoperable, powerful, robust and more flexible than traditional missions. Multiple satellites will bring increased revisit times and support a broad number of new applications for SAR imagery.
The RCM revisit cycle will change the way global disaster assessment and response operation planning are conducted.
Ready access to commercial SAR imagery and its inherent benefits for 24-hour acquisition and unique characteristics critical to many applications has made C-band SAR a vital component of global monitoring for civil and defense users. RCM will ensure at least another decade of data continuity and enhanced operational support for Canadian and international SAR data users.
Supporting Key Applications
As with the RADARSAT missions, RCM's SAR will be a key information source for a host of applications due to its imaging flexibility, accuracy of target detection and ability to detect minute vertical surface changes as well as its rapid tasking and revisit times, global access and wide variety of imaging capabilities.
In an era of increasingly violent weather patterns, SAR is a vital near real-time source of information to assess disaster impacts caused by flooding, earthquakes and landslides as well as to monitor and plan rescue efforts with its all-weather, day/night imaging capability.When time-critical information is needed, RCM has been designed to support rapid tasking of the satellites (5 hours from order to command uplink), real-time downlinks and rapid image delivery (10 minutes from downlink to delivery). Access to accurate and timely information used for actionable decision making is critical to effective disaster management applications, including mitigation, warning, response and recovery.
Operational support for the energy sector will include land and maritime applications, including oil detection on water around offshore operations, exploration, and risk mitigation. RCM's monitoring solutions for oil and gas help track the rate and direction of oil movement by providing information over a large area in any kind of weather, day or night. Such detailed information enables a more effective response to planning and damage mitigation in the event of an oil seep or spill. Using enhanced capabilities from RCM, oil seepage from the seafloor can be traced by identifying clusters of naturally occurring oil slicks.
Additionally, RCM can detect extremely small changes between image collections, enabling a wide range of applications such as subsidence detection, glacier motion studies, evaluation of faults before and after earthquakes, changes induced by climate change, vehicle displacement, land-use evolution, coastal changes, urban subsidence and even human impacts on local environments.
Ecosystem monitoring will include the ability to detect changes in forests, protected areas, wildlife habitats, agriculture, wetlands and coastal zones. Global governments and agribusinesses use SAR for more effective crop monitoring and crop identification applications, while regulatory agencies use it to monitor illegal fishing, forestry and pollution. Civil and military aviation agencies generate safer, optimized flight routes and landing procedures.
Canada's transition from individual Earth observation missions to a long-term sustainable space-radar constellation creates the opportunity for foreign partners to collaborate with the RCM program, which will further increase constellation capacity and repeat frequency. Challenges, such as determining the industrial component and establishing necessary bilateral relations with prospective contributing governments, will need to be addressed. Despite such challenges, the opportunity is real, and the potential benefits are significant.
A Snapshot of RCM Capabilities
The RADARSAT Constellation Mission (RCM) will continue the RADARSAT heritage of providing users with several operational advantages.
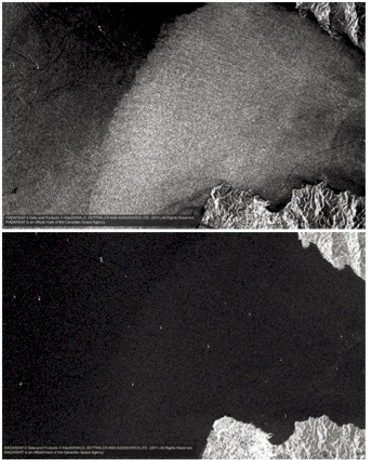
RCM's ability to capture wide areas of ocean using multiple polarizations enhances the ability to monitor ship movements. Here a RADARSAT-2 Wide 1 VV image (top) of the Straights of Gibraltar clearly shows ocean features and ship wakes. A Wide 1 VH polarization image (bottom) of the same area provides dramatically different information, showing ships and the land-water interface more clearly than the VV polarization image.
Widest Swath Widths
Like its predecessors, RCM will have a range of wide-area imaging modes to deliver cost-effective land and maritime coverage. For example, a single ScanSAR image can cover 250,000 km2.
Flexible Imaging Modes
RCM will support a wide variety of imaging modes, from wide-area surveillance using 500-km image swaths to spotlight modes at a ground resolution of one meter in azimuth and three meters in range.
Image Collection Frequency
As a three-satellite constellation, RCM will deliver high revisit frequency over areas of interest, providing users with more regular access to areas of interest, significantly altering the potential for global monitoring and change detection.
Multiple Polarization Capabilities
In addition to RADARSAT-2's selective single-, dual- and quad-polarization modes, RCM's new circular compact polarization will enable radar pulses to better detect surface features, target shapes and determine sea/ice boundaries. RCM's new compact polarimetric mode will receive dual linear H and V polarization, a design intended to provide many of the advantages of the quad-polarization (HH, VV, HV, VH) enhanced classification capabilities without the disadvantage of a reduced swath width. The images above illustrate the flexibility of using RADARSAT SAR polarization options for maritime monitoring using simultaneously collected imagery of an area of interest. One acquisition pass by the satellite yields a depth of information not available from any other existing mission.
Largest Imaging Capacity and Data Availability
RCM's three-satellite constellation represents a massive commercial capacity to ensure a high level of data availability, without risking substantial losses caused by resource constraints.


