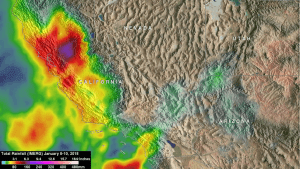
NASA's IMERG analysis of Jan. 8-10, 2018, revealed that the heaviest rainfall occurred over the Sacramento Valley, where more than 8 inches (203 millimeters) were indicated. A rainfall total of 5 inches (127 millimeters) was reported in Ventura County. (Credit: NASA/JAXA/Hal Pierce)
Winter rains falling on recently burned ground triggered deadly mudslides in Santa Barbara County, Calif., on Jan. 9, 2018. NASA recorded the amount of rainfall between Jan. 8-10, 2018, and calculated the potential for landslides. At least 17 residents of southern California were killed by the deadly mudslides.
At NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md., a landslide potential map was generated by the global Landslide Hazard Assessment for Situational Awareness (LHASA) model, which combines precipitation data from the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) satellite with a global landslide susceptibility map. LHASA gives a broad overview of landslide hazard in nearly real time, but site-specific information should be obtained prior to emergency operations or building projects.
A storm moving in from the Pacific Ocean dropped heavy rain over soil that was laid bare by recent wildfires. Heavy rainfall loosened surface sediments in Santa Barbara County on Jan. 9, causing the deadly mudslides.

