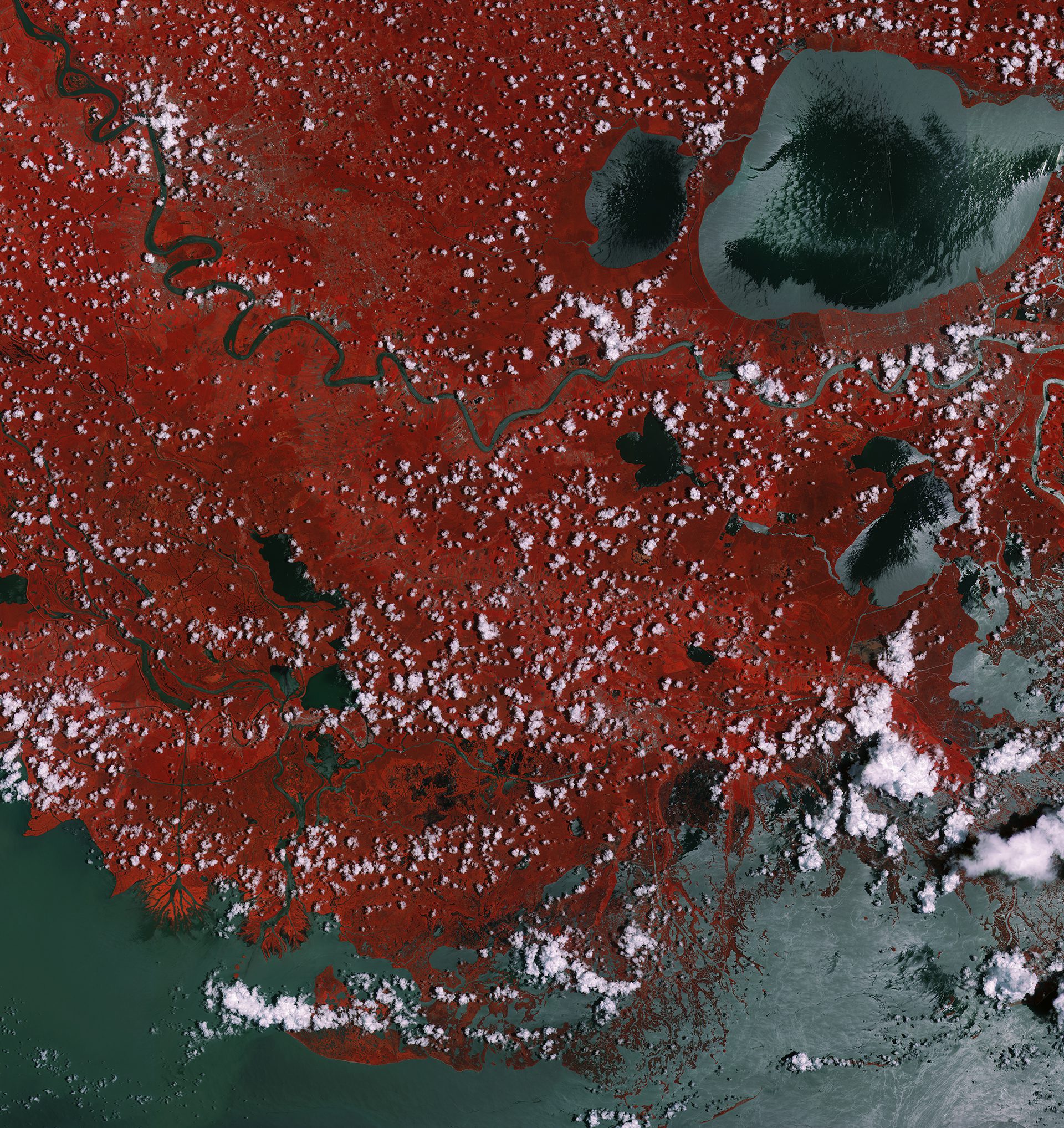
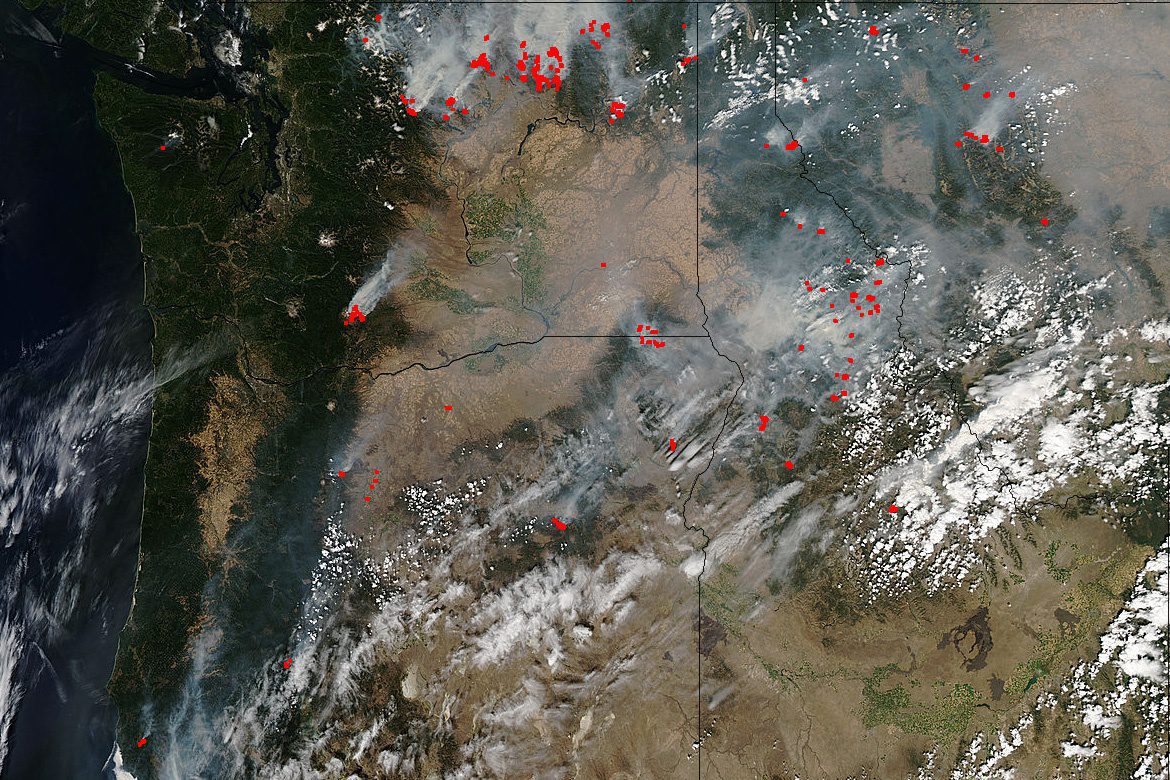
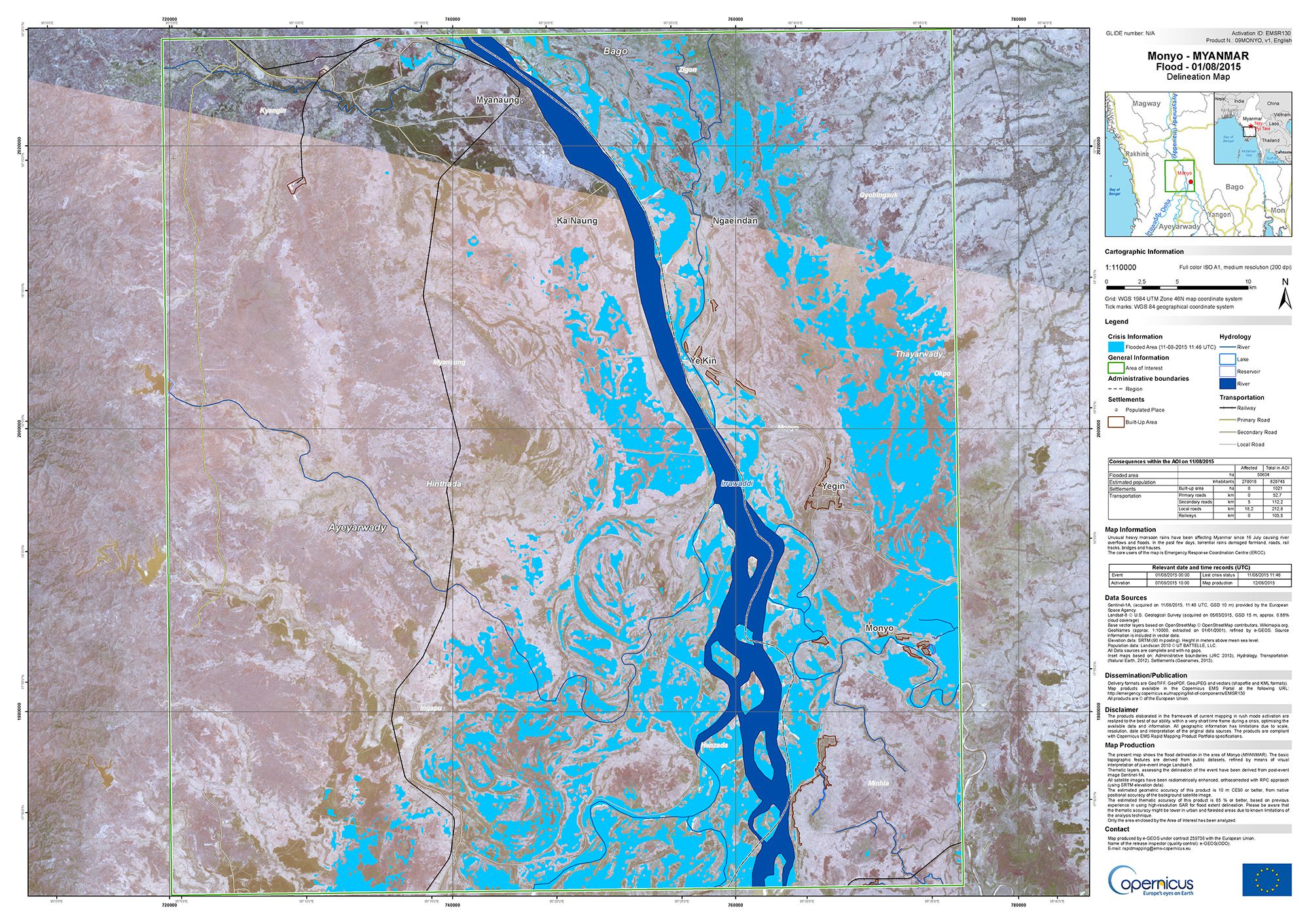
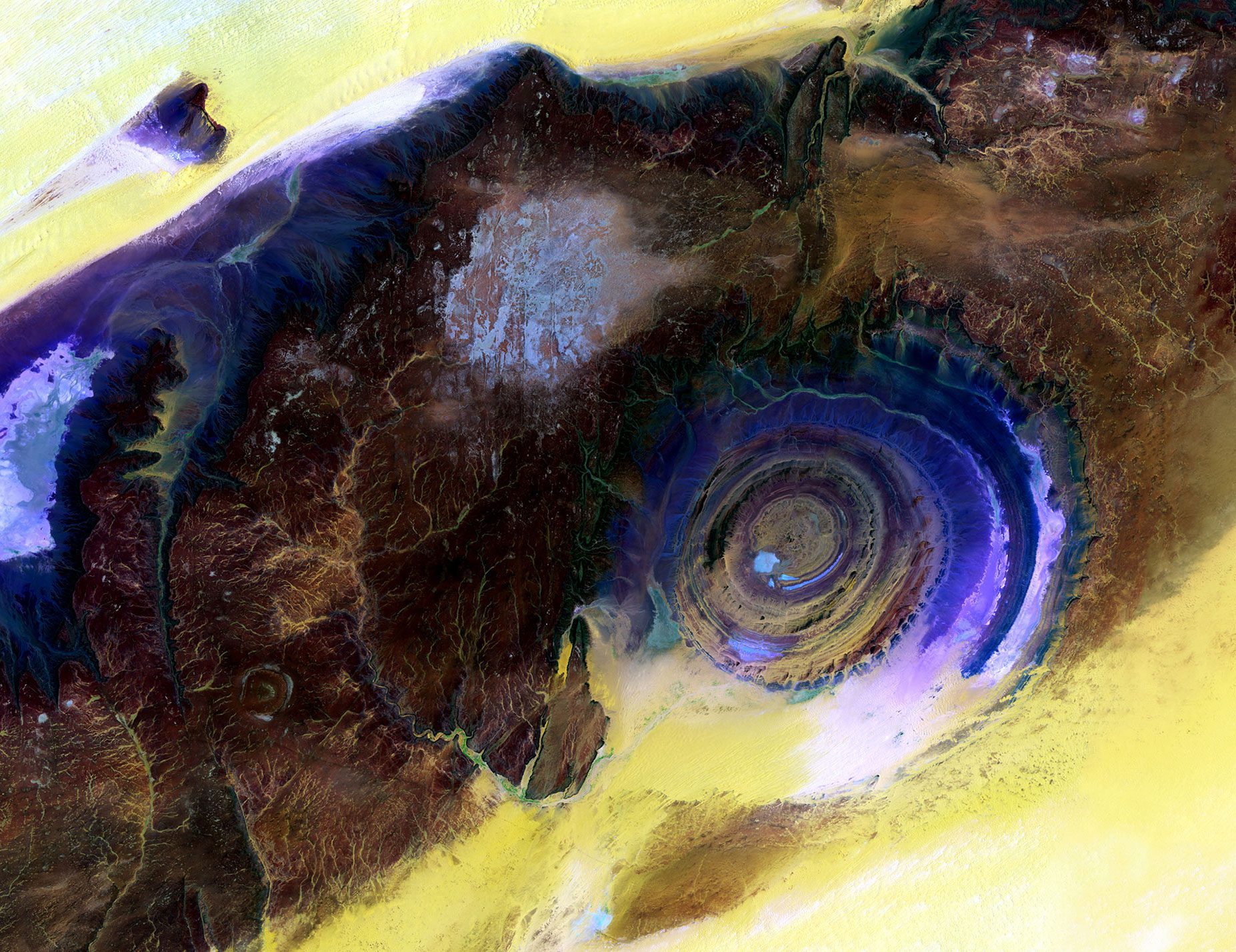
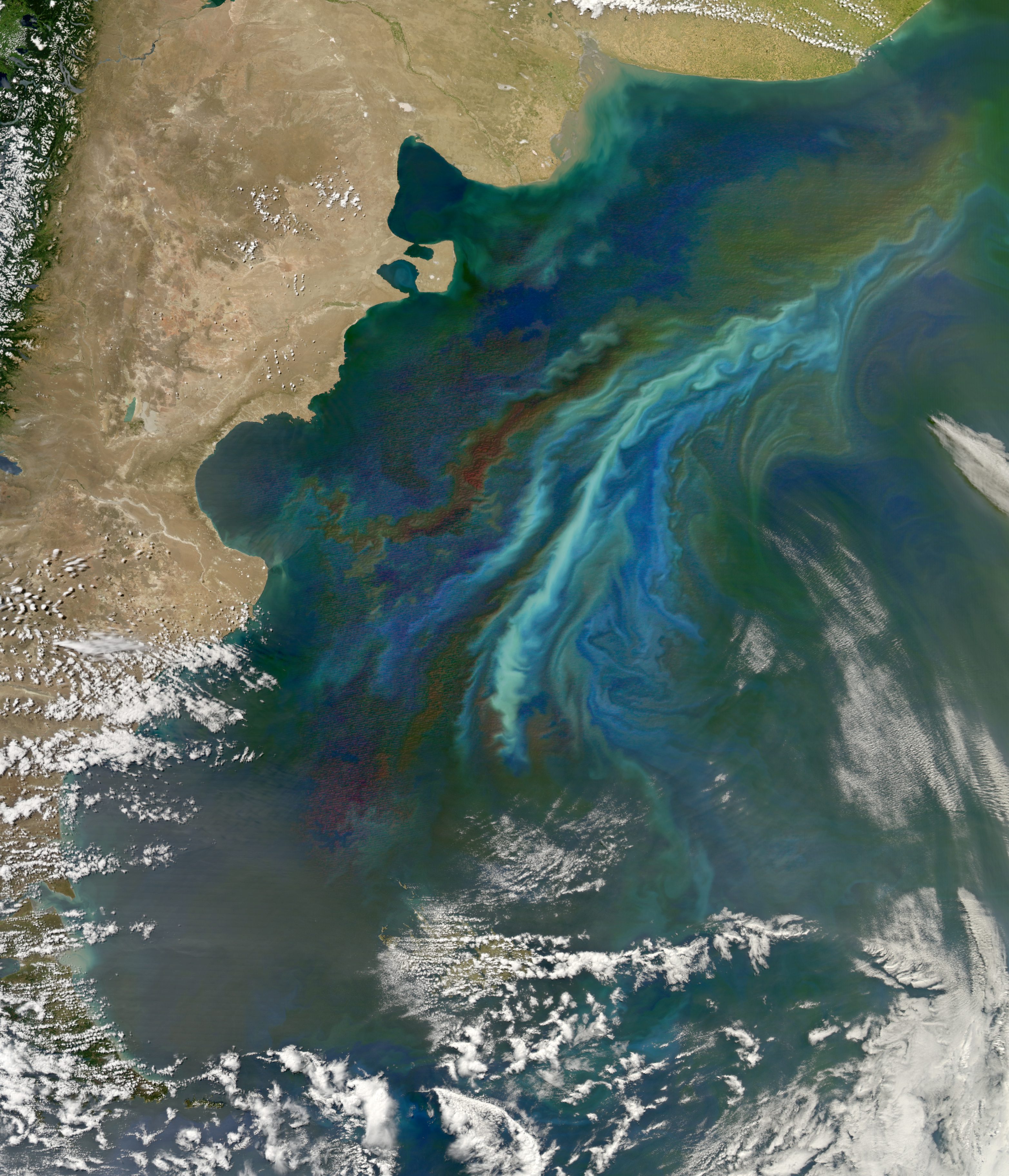
This Sentinel-2A ˜color vision' image captures part of the Mississippi swamps on the east and west banks of the Mississippi River, south of New Orleans and north of the Mississippi Delta. The red color shows vegetation, while gray represents bodies of water.